Penile Implant Innovations: The Latest Devices and Technologies
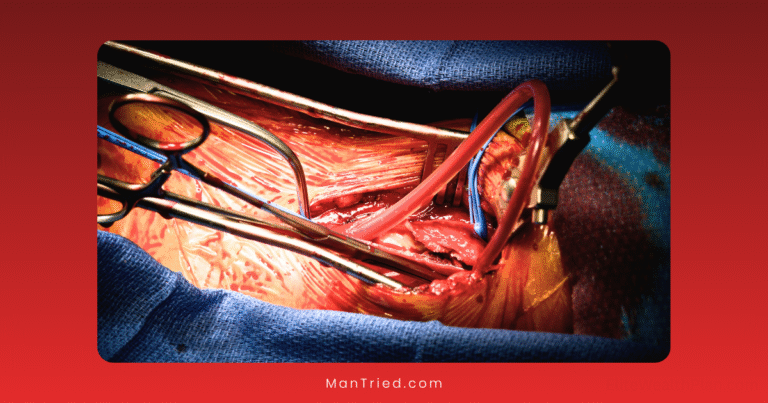
Erectile dysfunction (ED) affects millions of men worldwide, with projections suggesting over 322 million men will experience this condition by 2025. While first-line treatments like oral medications have revolutionized ED management, they aren’t effective for everyone. For men with severe ED who don’t respond to conservative approaches, penile implants represent the gold standard treatment—offering a reliable, on-demand solution with satisfaction rates exceeding 90%.
The field of penile implant technology has seen remarkable advancements in recent years, with innovations focused on improving reliability, reducing complications, enhancing user experience, and creating more natural results. This article explores the cutting-edge developments in penile implant technology and what the future may hold for this important treatment option.
The Evolution of Penile Implants
Before diving into recent innovations, it’s helpful to understand how penile implants have evolved over time.
Historical Context
The modern era of penile implants began in the early 1970s with the introduction of the first inflatable penile prosthesis (IPP) by American Medical Systems (AMS). Since then, these devices have undergone numerous iterations and improvements.
“The basic concept of the three-piece inflatable penile prosthesis hasn’t changed dramatically since its introduction,” explains Dr. Ricardo Munarriz, Professor of Urology at Boston University School of Medicine. “However, the materials, mechanical reliability, and design features have been continuously refined to address complications and improve patient experience.”
Types of Penile Implants
Currently, there are three main categories of penile implants:
- Malleable (Semi-Rigid) Penile Prostheses
- Consist of paired rods implanted within the corpora cavernosa
- Always firm but can be bent into different positions
- Simpler surgery with fewer components
- Lower cost and mechanical failure rates
- Examples: AMS Spectra, Coloplast Genesis
- Two-Piece Inflatable Penile Prostheses
- Include cylinders and a combined pump/reservoir
- Allow for inflation and deflation
- No separate abdominal reservoir required
- Example: AMS Ambicor
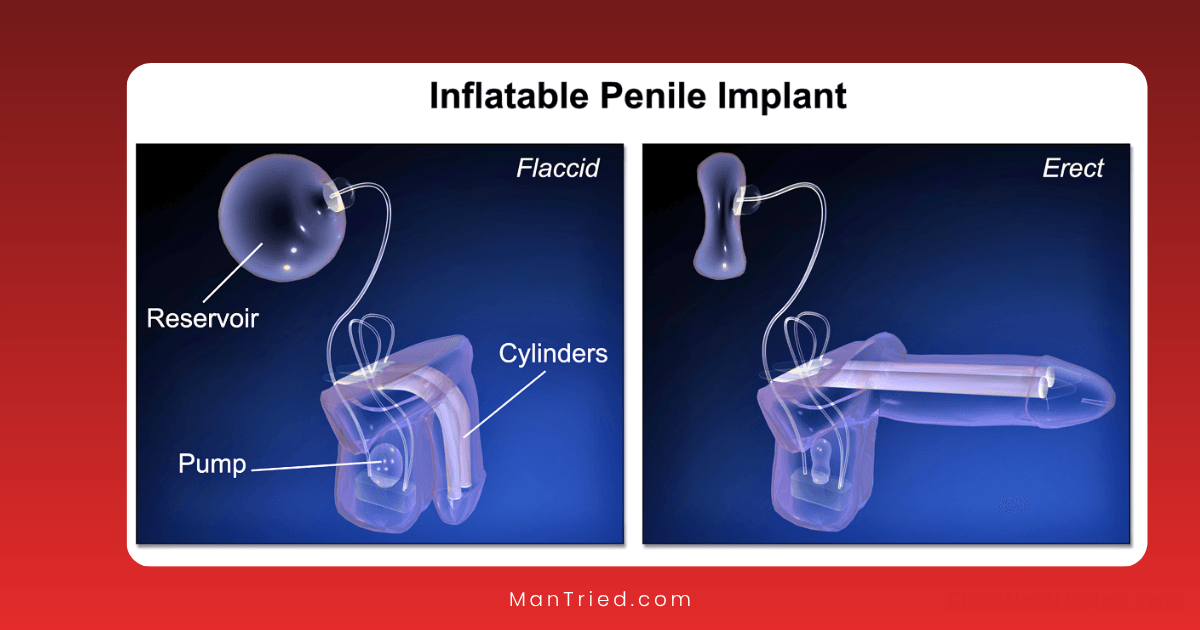
- Three-Piece Inflatable Penile Prostheses
- Most natural in appearance and function
- Include cylinders, scrotal pump, and abdominal fluid reservoir
- Provide the best rigidity and flaccidity
- Examples: AMS 700series, Coloplast Titan
According to research published in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, three-piece inflatable devices are the most commonly used in the United States and other developed countries, accounting for approximately 75% of all implants.
Recent Innovations in Penile Implant Technology
The past decade has seen significant advancements in penile implant technology across several domains:
1. Improved Materials and Durability
Enhanced Cylinder Materials
The Bioflex® material used in Coloplast’s Titan cylinders has increased tensile strength by seven times compared to earlier materials, resulting in significantly improved durability. According to a long-term study published in the Journal of Urology, 88% of Titan implants remained operational after 10 years.
Similarly, Boston Scientific (formerly AMS) has introduced Parylene Micro Coating for their 700 Series cylinders, which enhances durability by reducing wear on the silicone material.
Advanced Pump Mechanisms
The TENACIO™ Pump, recently introduced by Boston Scientific for the AMS 700™ Inflatable Penile Prosthesis, represents a significant advance in usability. According to Boston Scientific’s news release, this redesigned pump features:
- Exaggerated grips for easier handling, especially beneficial for older patients
- An elongated neck between inflation and deflation buttons for better tactile differentiation
- Independent valve systems that accommodate various squeezing speeds and pressures
Similarly, Coloplast’s “One-Touch Release” (OTR) pump allows patients to deflate the device with a single squeeze, significantly improving ease of use.
2. Infection Prevention Technologies
Infection remains one of the most serious potential complications of penile implant surgery. Recent innovations have dramatically reduced infection rates:
Antibiotic Coatings
InhibiZone®, developed by AMS/Boston Scientific, incorporates rifampin and minocycline into the external surfaces of the implant. According to a multicenter clinical study published in the Journal of Urology, this technology reduced postoperative infections by 82.4% compared to non-coated implants.
Hydrophilic Coatings
Coloplast’s Titan features a hydrophilic coating that absorbs antibiotics when soaked in an antibiotic solution during surgery. This approach allows surgeons to customize the antibiotic coverage based on patient needs and local bacterial resistance patterns.
“These infection-reducing technologies represent one of the most significant advances in penile implant surgery,” notes Dr. Paul Perito, a urologist specializing in penile implants. “We’ve seen infection rates drop from historical levels of 2-3% to less than 1% in many high-volume centers.”
3. Size and Expansion Capabilities
Length and Girth Expansion
The AMS LGX® (Length and Girth eXpansion) model offers a unique bidirectional dacron sleeve that allows for expansion in both length and girth—up to 25% in each dimension. This provides a more natural erection and potentially better size restoration for patients who have experienced penile shortening due to conditions like Peyronie’s disease or prostatectomy.
Cylinder Size Options
Both major manufacturers now offer expanded cylinder size options to better accommodate different anatomies:
- Coloplast Titan cylinders are available in lengths of 10-28cm
- AMS 700 series offers cylinders from 12-24cm
- Both manufacturers provide various diameter options and rear tip extenders for precise sizing
Dr. Rafael Carrion, Professor of Urology at USF Health, explains: “The expanded range of sizes allows for much better customization to individual patient anatomy, which translates to improved comfort and satisfaction.”
4. Mechanical Reliability Improvements
Auto-Inflation Prevention
Coloplast’s Lock-out™ valve and Boston Scientific’s similar technology address the problem of auto-inflation—spontaneous filling of the cylinders during physical activity, which was a common complaint with earlier models.
These innovations minimize fluid transfer under abdominal pressure, significantly reducing episodes of embarrassing auto-inflation while maintaining proper function when intentionally activated.
Kink-Resistant Tubing
Both manufacturers have developed reinforced, kink-resistant tubing that connects the components of three-piece implants. This seemingly simple improvement has significantly reduced mechanical failure rates by preventing tubing occlusion—previously a common cause of device malfunction.
The Future of Penile Implant Technology
The penile implant market continues to evolve, with several promising innovations on the horizon:
1. Smart Implants
Researchers are exploring the integration of electronic components that would allow for:
- Remote control operation via smartphone apps
- Pressure and position sensing for more natural control
- Customizable settings for individual preferences
- Telemedicine capabilities for remote troubleshooting
While still primarily in development stages, these “smart implants” could represent the next major leap forward in the field.
2. Advanced Materials Science
Shape Memory Alloys
Nickel-titanium alloys (Nitinol) and other shape memory materials are being investigated for use in penile implants. These materials could potentially allow for:
- Temperature-activated changes in rigidity
- Reduced mechanical complexity
- Improved durability and longevity
- More natural feel and function
3D-Printed Custom Implants
According to a review in the Journal of Sexual Medicine, the future may include custom-designed implants based on individual patient anatomy:
- 3D imaging of the patient’s penile anatomy
- Computer-aided design of perfectly sized components
- 3D printing of customized implants
- Potentially improved outcomes through precise anatomical matching
3. Tissue Engineering Approaches
Perhaps the most futuristic approach involves tissue engineering and regenerative medicine:
- Scaffolds seeded with the patient’s own cells
- Growth of functional erectile tissue
- Potential for a fully biological solution
- Integration with the body’s natural systems
Dr. Anthony Atala, Director of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine, notes: “While still experimental, the combination of tissue engineering with implant technology could eventually lead to hybrid solutions that offer the reliability of implants with more natural tissue integration.”
4. Expanding Global Access
The global penile implant market is projected to reach $686 million by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 4.7%. However, access remains limited in many regions.
Future innovations are likely to include:
- More cost-effective designs for developing markets
- Simplified surgical techniques requiring less specialized training
- Telemedicine support for surgeons in remote areas
- Culturally sensitive education and awareness programs
Patient Considerations and Outcomes
Despite technological advances, penile implants remain significantly underutilized. Less than 5% of eligible patients with refractory ED opt for implantation, often due to lack of awareness, cost concerns, or anxiety about the procedure.
Satisfaction Rates
Modern penile implants consistently demonstrate exceptional satisfaction rates:
- Patient satisfaction: 90-95%
- Partner satisfaction: 85-90%
- Functional success rate: >90%
- 10-year device survival: 60-88% (depending on model)
A systematic review in the Journal of Sexual Medicine found that penile implants provided higher satisfaction rates than any other ED treatment, including oral medications, injections, or vacuum devices.
Cost Considerations
The cost of penile implant surgery varies significantly:
- Device cost: $10,000-$20,000
- Surgical fees: $6,000-$15,000
- Hospital/facility fees: $5,000-$15,000
- Total cost without insurance: $20,000-$50,000
Many insurance plans, including Medicare, cover penile implants when medically necessary, though coverage policies vary widely.
Conclusion
Penile implant technology continues to advance rapidly, with innovations focused on improving reliability, reducing complications, enhancing user experience, and creating more natural results. For men with severe erectile dysfunction who don’t respond to other treatments, these devices offer a highly effective solution with exceptional satisfaction rates.
As awareness grows and technology continues to improve, penile implants are likely to become an increasingly important option in the management of erectile dysfunction. The future promises even more exciting developments that may further enhance this already successful treatment approach.